| [1]Zhou CP, Zhou ZK, Shen B, et al. Zhonghua Guanjie Waike Zazhi(Dianziban). 2012;6(5):23-26.周程沛,周宗科,沈彬,等. 膝关节类风湿关节炎伴重度屈曲畸形患者关节置换术后的中长期随访[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2012,6(5):23-26.[2]Wang TJ, Wang B, Lv HS. Zhongguo Yishi Jinxiu Zazhi. 2012; 35(32):21-23.王铁军,王波,吕厚山. 膝关节骨性关节炎与类风湿关节炎患者全膝人工关节置换术术前检查的区别及注意事项[J].中国医师进修杂志,2012,35(32):21-23.[3]Zhang YD, Gao MJ, Wang RM, et al. Zhonguo laonianxue Zazhi. 2012;32(21): 4795-4796.张永东,高默杰,王瑞珉,等.人工全膝关节置换在中老年类风湿关节炎中的应用[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(21): 4795-4796.[4]Yao J, Zhao Y, Zhong CL. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(13):2389-2398.姚进,赵允,仲丛丽. 髋关节置换研究:Scopus数据库5年文献检索与分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(13):2389-2398.[5]Mullaji AB, Marawar SV. Primary total hip arthroplasty in protrusio acetabuli using impacted morsellized bone grafting and cementless cups: a medium-term radiographic review. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(8):1143-1149.[6]Mochida Y, Saito I, Akamatsu Y, et al. Clinical and radiological results of non-cement impaction bone-graft method of total hip arthroplasty for rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2007; 17(3):235-238.[7]Gerber SD, Harris WH. Femoral head autografting to augment acetabular deficiency in patients requiring total hip replacement. A minimum five-year and an average seven-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986;68(8): 1241-1248.[8]Guo TY, Zhou JS. Zhongguo Guy u Guanjie Sunshang Zazhi. 2013,28(2):196-198.郭通亚,周建生.人工全髋关节翻修术中髋臼缺损重建的研究进展[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(2):196-198.[9]Yuan MW, Pan J, Zhang XD. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(39):7227-7231.袁明武,潘江,张晓冬.全髋关节置换并结构性植骨治疗CroweⅢ型髋臼发育不良性骨关节炎[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(39): 7227-7231.[10]Chen ZW, Yuan J, Cao SJ, et al. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2012;26(3):292-294.陈志伟,袁杰,曹盛俊,等.人工全髋关节置换治疗髋臼内陷症的早期疗效[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(3):292-294.[11]Gusis SE, Maldonado Cocco JA, et al. Protrusio acetabuli in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 1993;12(1): 36-40.[12]Ries MD. Total hip arthroplasty in acetabular protrusio. Orthopedics. 2009;32(9):708-712.[13]Garcia-Cimbrelo E, Diaz-Martin A, Madero R, et al. Loosening of the cup after low-friction arthroplasty in patients with acetabular protrusion. The importance of the position of the cup. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(1):108-115.[14]Blumenfeld TJ, Bargar WL. Surgical technique: a cup-in-cup technique to restore offset in severe protrusio acetabular defects. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(2):435-441.[15]Sochart DH, Porter ML. Long-term results of total hip replacement in young patients who had ankylosing spondylitis. Eighteen to thirty-year results with survivorship analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(8):1181-1189. [16]Bayley JC, Christie MJ, Ewald FC, et al. Long-term results of total hip arthroplasty in protrusio acetabuli. J Arthroplasty. 1987;2(4):275-279. [17]Krushell RJ, Fingeroth RJ, Gelling B. Primary total hip arthroplasty using a dual-geometry cup to treat protrusio acetabuli. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(8):1128-1131.[18]Gaiani L, Bertelli R, Palmonari M,et al. Total hip arthroplasty revision in elderly people with cement and Burch-Schneider anti-protrusio cage. Chir Organi Mov. 2009;93(1):15-19[19]Borland WS, Bhattacharya R, Holland JP,et al. Use of porous trabecular metal augments with impaction bone grafting in management of acetabular bone loss. Acta Orthop. 2012; 83(4):347-352.[20]Figueras Coll G, Salazar Fernandez de Erenchu J, Roca Burniol J. Results of acetabular wiremesh and autograft in protrusio acetabuli. Hip Int. 2008;18(1):23-28.[21]Mibe J, Imakiire A, Watanabe T, et al. Results of total hip arthroplasty with bone graft and support ring for protrusio acetabuli in rheumatoid arthritis. J Orthop Sci. 2005;10(1):8-14.[22]Rosenberg WW, Schreurs BW, de Waal Malefijt MC, et al. Impacted morsellized bone grafting and cemented primary total hip arthroplasty for acetabular protrusion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: an 8- to 18-year follow-up study of 36 hips. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71(2):143-146.[23]Patil N, Hwang K, Goodman SB. Cancellous impaction bone grafting of acetabular defects in complex primary and revision total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2012;35(3): e306-312.[24]Garcia-Cimbrelo E, Cruz-Pardos A, Garcia-Rey E ,et al. The survival and fate of acetabular reconstruction with impaction grafting for large defects. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468(12):3304-3313.[25]Dutka J, Sosin P, Skowronek P,et al. Total hip arthroplasty with bone grafts for protrusio acetabuli. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2011;13(5):469-477. [26]Cichý Z. Treatment of dysplastic acetabulum using total hip arthroplasty: our intermediate-term results. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2006;73(5):340-344.[27]Heywood AW. Arthroplasty with a solid bone graft for protrusio acetabuli. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1980;62(3):332-336.[28]Slooff TJ, Huiskes R, Van Hom J, et al. Bone grafting in total hip replacement for acetabular protrusion. Acta Orthop Scand. 1984;55(6):593-596.[29]Rosenberg WW, Schreurs BW, de Waal Malefijt MC,et al. Impacted morsellized bone grafting and cemented primary total hip arthroplasty for acetabular protrusion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: an 8- to 18-year follow-up study of 36 hips. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71(2):143-146. [30]Busch VJ, Gardeniers JW, Verdonschot N, et al. Acetabular reconstruction with impaction bone-grafting and a cemented cup in patients younger than fifty years old: a concise follow-up, at twenty to twenty-eight years, of a previous report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(4):367-371.[31]Welten ML, Schreurs BW, Buma P, et al. Acetabular reconstruction with impacted morcellized cancellous bone autograft and cemented primary total hip arthroplasty: a 10- to 17-year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15(7):819-824. [32]Rosenberg AWJ, Schreurs WB, et al. Impaceted morsellized bone grafting and cemented primary total hip arthroplasty for acetabular protrusion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Orthop Scand,2000;71:143[33]Schulte KR, Callaghan JJ, Kelley SS, et al. The outcome of Charnley total hip arthroplasty with cement after a minimum twenty-year follow-up. The results of one surgeon. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(7):961-975.[34]Ballard WT, Callaghan JJ, Sullivan PM, et al. The results of improved cementing techniques for total hip arthroplasty in patients less than fifty years old. A ten-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76(7):959-964.[35]Barrack RL, Mulroy RD Jr, Harris WH. Improved cementing techniques and femoral component loosening in young patients with hip arthroplasty. A 12-year radiographic review. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992;74(3):385-389.[36]Busch VJ, Gardeniers JW, Verdonschot N,et al. Acetabular reconstruction with impaction bone-grafting and a cemented cup in patients younger than fifty years old: a concise follow-up, at twenty to twenty-eight years, of a previous report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(4):367-371.[37]Clohisy JC, Harris WH. Matched pair analysis of cemented and cementless acetabular reconstruction in primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2002;16(6):697-705.[38]Berend ME. Acetabular protrusio: a problem in depth. Orthopedics. 2008;31(9):895-896.[39]Berger RA, Jacobs JJ, Quigley LR, et al. Primary cementless acetabular reconstruction in patients younger than 50 years old. 7- to 11-year results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997; (344): 216-226.[40]Matsuno H, Yasuda T, Yudoh K,et al. Cementless cup supporter for protrusio acetabuli in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int Orthop. 2000;24(1):15-18.[41]Wang YG, Tang BS. Zhongguo Shiyong Yiyao. 2011;6(32): 30-32.王永贵,唐本森. 全髋关节置换术治疗类风湿性髋关节炎的临床观察[J].中国实用医药,2011,6(32):30-32.[42]Chen LJ, Zhang Y. Zhonghua Guanjie Waike Zazhi (Dianziban). 2011;5(1):55-58.陈林建,张毅.人工全髋关节置换术髋臼杯准确安放的影响因素[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2011,5(1):55-58.[43]Lundby R, Kirkhus E, Hald J, et al. CT of the hi ps in the investigation of protrusio acetabuli in Marfan syndrome. A case control study. Eur Radiol. 2011;21(7):1485-1491.[44]Sun JW, Yin WP, Zhang C, et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(22):4006-4009.孙剑伟,尹望平,张春,等.髋臼区域皮质骨厚度分布特征的三维图像测量[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(22):4006-4009.[45]Li DS, Li SQ, Cai B, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(48): 9104-9108.李冬松,李叔强,蔡波,等.成人髋臼发育不良髋臼内壁内移截骨的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(48): 9104-9108.[46]Xiang SS, Chen Y, Fu M, et al. ZHonghua Guanjie Waike Zazhi(Dianziban). 2012;6(3):68-71.向珊珊,陈艺,傅明,等.髋臼旋转截骨术时髋臼后上方植骨前后髋关节生物力学的改变及其对比[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2012,6(3):68-71. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
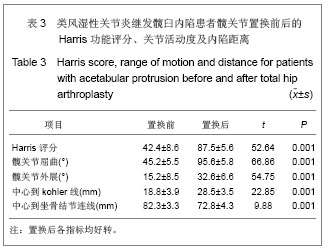
.jpg) 对髋臼内陷的类风关患者行关节置换时,必须尽量将髋臼假体外移至关节正常结构位置,恢复髋关节正常运动中心, 这样可以明显降低髋臼假体松动发生率[11] 。髋臼假体旋转中心到髋关节运动中心的距离是影响术后假体松动的最重要的因素[12-14] ,Sochart和Porter等[15]平均22.7年的长期随访发现,人工股骨头中心与髋关节的正常解剖中心距离越近,髋臼假体出现松动的发生率越低。Bayley等[16]研究表现,髋臼内陷患者髋关节置换后,运动中心恢复良好的远期生存率高,运动中心恢复到解剖外置,松动率仅为8%,而运动中心与解剖中心的距离大于10 mm,髋臼假体松动率将高达50%。
对髋臼内陷的类风关患者行关节置换时,必须尽量将髋臼假体外移至关节正常结构位置,恢复髋关节正常运动中心, 这样可以明显降低髋臼假体松动发生率[11] 。髋臼假体旋转中心到髋关节运动中心的距离是影响术后假体松动的最重要的因素[12-14] ,Sochart和Porter等[15]平均22.7年的长期随访发现,人工股骨头中心与髋关节的正常解剖中心距离越近,髋臼假体出现松动的发生率越低。Bayley等[16]研究表现,髋臼内陷患者髋关节置换后,运动中心恢复良好的远期生存率高,运动中心恢复到解剖外置,松动率仅为8%,而运动中心与解剖中心的距离大于10 mm,髋臼假体松动率将高达50%。
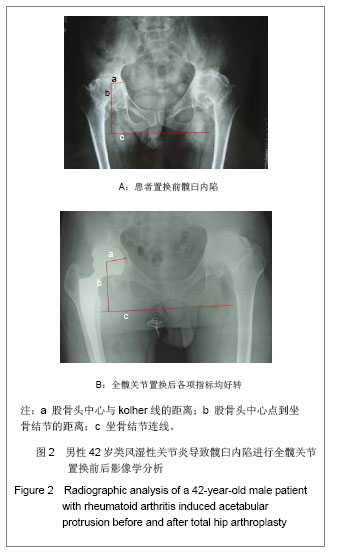
.jpg) 自体移植骨打压,使用非骨水泥固定的假体是类风关继发髋臼内陷行髋关节置换手术的良好选择,这样既可以恢复髋臼内陷时的骨量缺损,使假体外置至接近正常髋关节运动中心,符合髋关节正常生物力学,又能为髋臼假体提供一个更适合的生物型固定方式[44-46] 。从实验对该组病例的近期随访资料来看,此种方法简单有效,可获得良好的疗效,能有效防止假体松动及再次内陷,长期效果仍有待于进一步观察。
自体移植骨打压,使用非骨水泥固定的假体是类风关继发髋臼内陷行髋关节置换手术的良好选择,这样既可以恢复髋臼内陷时的骨量缺损,使假体外置至接近正常髋关节运动中心,符合髋关节正常生物力学,又能为髋臼假体提供一个更适合的生物型固定方式[44-46] 。从实验对该组病例的近期随访资料来看,此种方法简单有效,可获得良好的疗效,能有效防止假体松动及再次内陷,长期效果仍有待于进一步观察。